This is the RPy demo from rpy.sf.net adjusted for the L3 worksheet
interface1. In particular, all print statements displaying
data are removed (they are not needed with interactive data
viewing), and the print commands providing header information are
turned into outline headers (when viewing data next to the source,
there is no need to replicate this information).
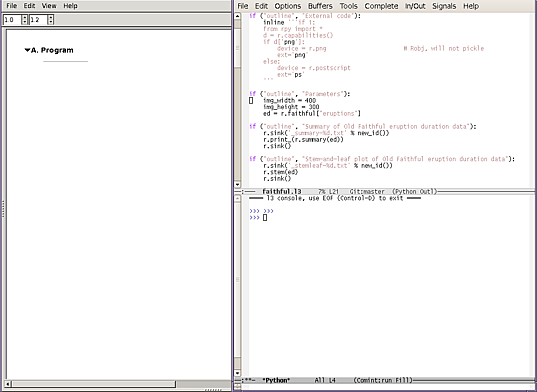
1 Start with the script
Starting point for this demo is the script, produced as usual via a text editor; it contains far too much detail to make graphical editing practical:
if ("outline", "External code"):
inline '''if 1:
from rpy import *
d = r.capabilities()
if d['png']:
device = r.png
ext='png'
else:
device = r.postscript
ext='ps'
'''
if ("outline", "Parameters"):
img_width = 400
img_height = 300
ed = r.faithful["eruptions"]
if ("outline", "Summary of Old Faithful eruption duration data"):
r.sink('_summary-%d.txt' % new_id())
r.print_(r.summary(ed))
r.sink()
if ("outline", "Stem-and-leaf plot of Old Faithful eruption duration data"):
r.sink('_stemleaf-%d.txt' % new_id())
r.stem(ed)
r.sink()
if ("outline", "Old Faithful eruptions"):
file = 'faithful_histogram-%d.%s' % (new_id(), ext)
device(file, width=img_width, height=img_height)
r.hist(ed,r.seq(1.6, 5.2, 0.2), prob=1,col="lightgreen",
main="Old Faithful eruptions",
xlab="Eruption duration (seconds)")
r.lines(r.density(ed,bw=0.1),col="orange")
r.rug(ed)
r.dev_off()
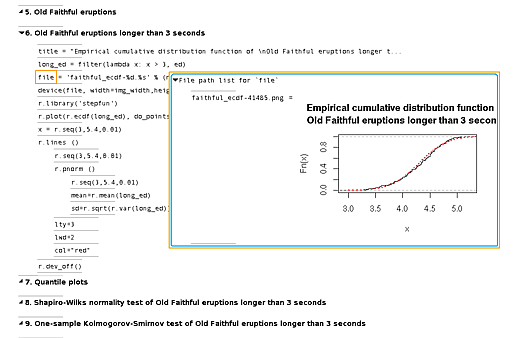
if ("outline", "Old Faithful eruptions longer than 3 seconds"):
title = "Empirical cumulative distribution function of \nOld Faithful eruptions longer than 3 seconds"
long_ed = filter(lambda x: x > 3, ed)
file = 'faithful_ecdf-%d.%s' % (new_id(), ext)
device(file, width=img_width,height=img_height)
r.library('stepfun')
r.plot(r.ecdf(long_ed), do_points=0, verticals=1, main = title)
x = r.seq(3,5.4,0.01)
r.lines(r.seq(3,5.4,0.01),
r.pnorm(r.seq(3,5.4,0.01),
mean=r.mean(long_ed), sd=r.sqrt(r.var(long_ed))),
lty=3, lwd=2, col="red")
r.dev_off()
if ("outline", "Quantile plots"):
file = 'faithful_qq-%d.%s' % (new_id(), ext)
device(file, width=img_width, height=img_height)
r.par(pty="s")
r.qqnorm(long_ed, col="blue")
r.qqline(long_ed, col="red")
r.dev_off()
if ("outline", "Shapiro-Wilks normality test of Old Faithful eruptions longer than 3 seconds"):
r.library('ctest')
sw = r.shapiro_test(long_ed)
if ("outline", "One-sample Kolmogorov-Smirnov test of Old Faithful eruptions longer than 3 seconds"):
ks = r.ks_test(long_ed,"pnorm", mean=r.mean(long_ed),
sd=r.sqrt(r.var(long_ed)))
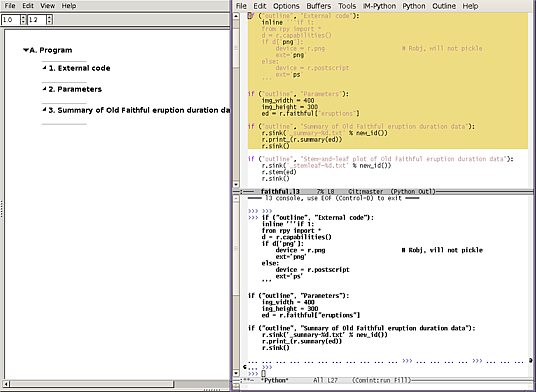
2 Move the script into the worksheet
This could be loaded all at once but for exploration working with one
section at a time is better. Using edit > L3 terminal console, get
a console on the terminal RPy was started from. There are now three
windows, the source code, the terminal, and the gui:
The gui accumulates the expressions entered into the terminal. After copying the first three outlines, this is
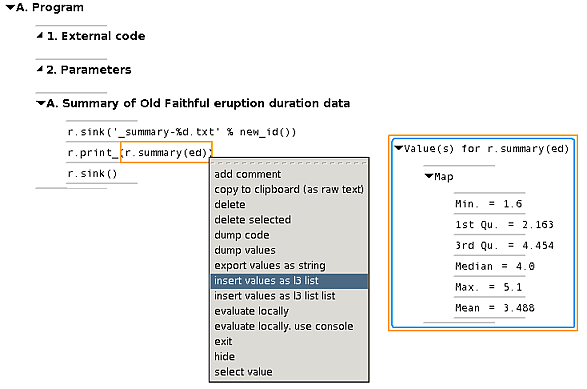
3 Examine key-value data
By expanding the outline, we see the three code lines; the r.sink
command put plain text output into a file (which we can inspect if
desired). But to just view the results, a simple menu selection is
enough:
This brings the script and its output together in one place and there is
no redundant information – the header describes what we're looking
at, without additional print statements to provide the same
information in the output.
4 View some graphs
The graphical abilities of R can be used similarly. Running the whole script first, we can selectively view plots. In the following image, we see the script section setting plot parameters on the left, with the (generated) file name and contents on the right:
Again, the script and the output are together, so we don't have to manually make the association between several graphs on one side and multiple script fragments on the other.
-----------Footnotes:
1 This demo requires R and RPy to be installed. Your system's package handler may provide these, e.g.
apt-get install python-rpyon Ubuntu or Debian GNU/Linux or
yum install rpyon Fedora 6 or newer systems. The self-contained L3 installer also has rules for installing these locally. The commands
cd <path to installer>/bindings/rpy make installwill download, compile and "install" rpy and dependencies. Note that a FORTRAN compiler is required.